Software installation is an vital part while working on any operating system. Installing applications on Windows Operating system is very straight forward as you just need to double click on the executable file and follow the subsequent prompts and that's all!
On Unix and Linux it's totally a different ball game. How it is different than Windows, how to configure repositories etc. In this article I will be demonstrating the end to end process of repository and software management process on Linux.
What are Software Repositories?
All the Linux distributions hosts their own software repositories. A Linux user no need to go to vendor's websites in order to download the applications unlike on Windows.
It's a centralized storage location from where the Linux systems retrieves, installs software updates and applications. These repositories contains specially compiled packages in accordance with the OS distribution and version.
What are Package Managers?
Package Manager is a tool which enables a Linux user to download, install, uninstall or upgrade software packages in an automated manner.
They play a very crucial role in Linux software management. They keep tracks of all the software's installed on you system and notify you whenever a new update or upgrade is available for an application or for the Operating system itself.
Every Linux distribution for example Ubuntu, Red Hat or Arch Linux everyone has their own Package Manager tools. We will discuss about this in coming sections.
What is a Package?
A package contain all of the necessary files, meta-data, and instructions to implement a particular functionality or software application on your system.
Package Management on Ubuntu Linux
Ubuntu’s has a very comprehensive and extremely matured package management system which is originally acquired from the Debian Linux distribution.
Configuring Software repositories on an Ubuntu System
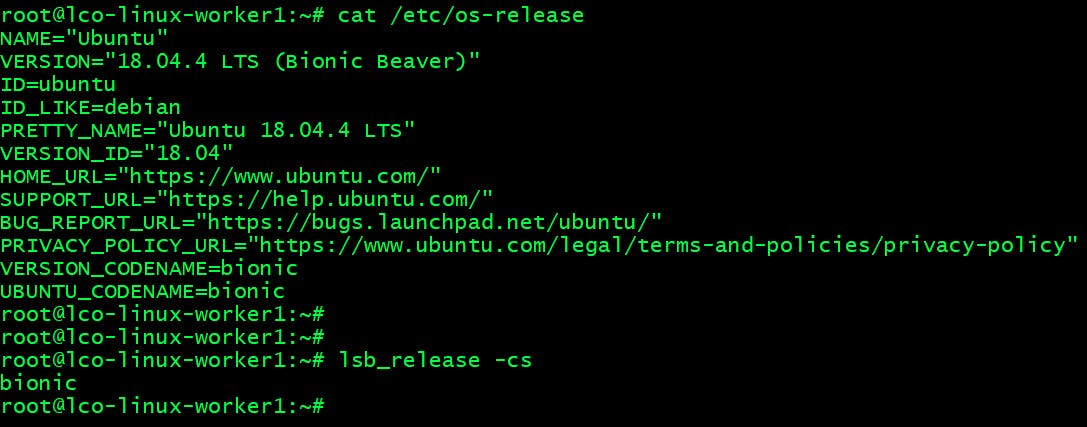
I am using Ubuntu 18.04 LTS system for this demo purpose.
The place to configure software repositories on all Debian based operating systems like Ubuntu is either in /etc/apt/sources.list file or can be configured in separate files under the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory. The name of the files must end with .list extension.
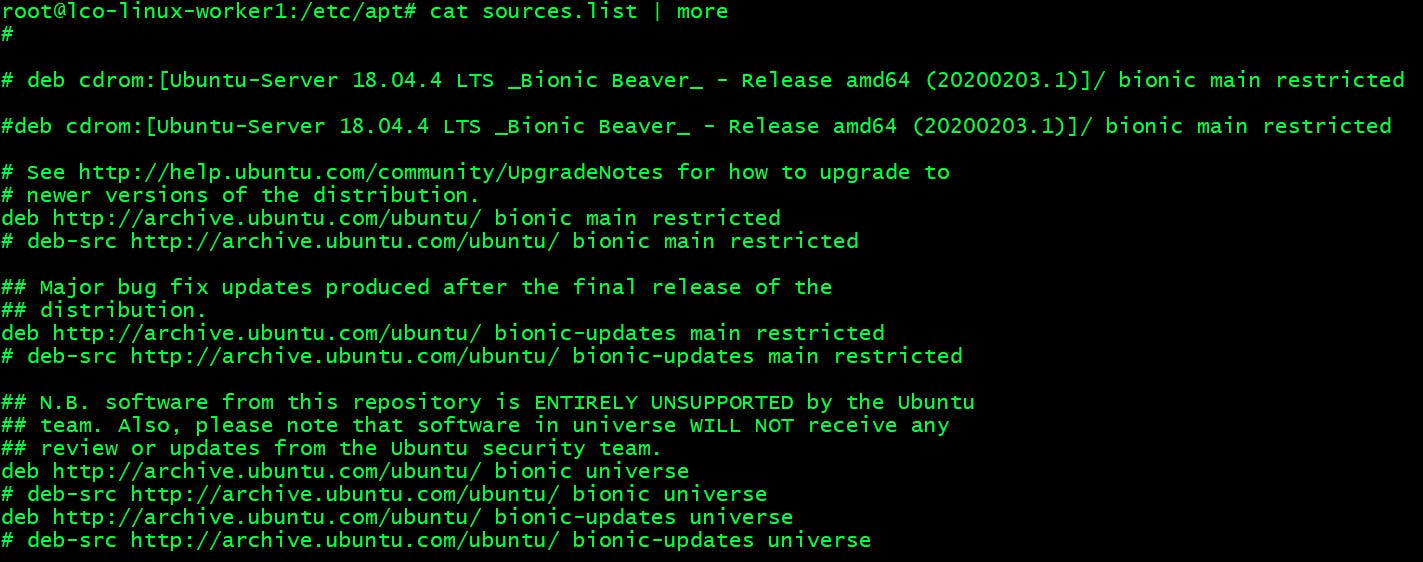
Lines starting with hash (#) are comments which are used for documentation purposes. Comments can also be used to disable a certain package repository.
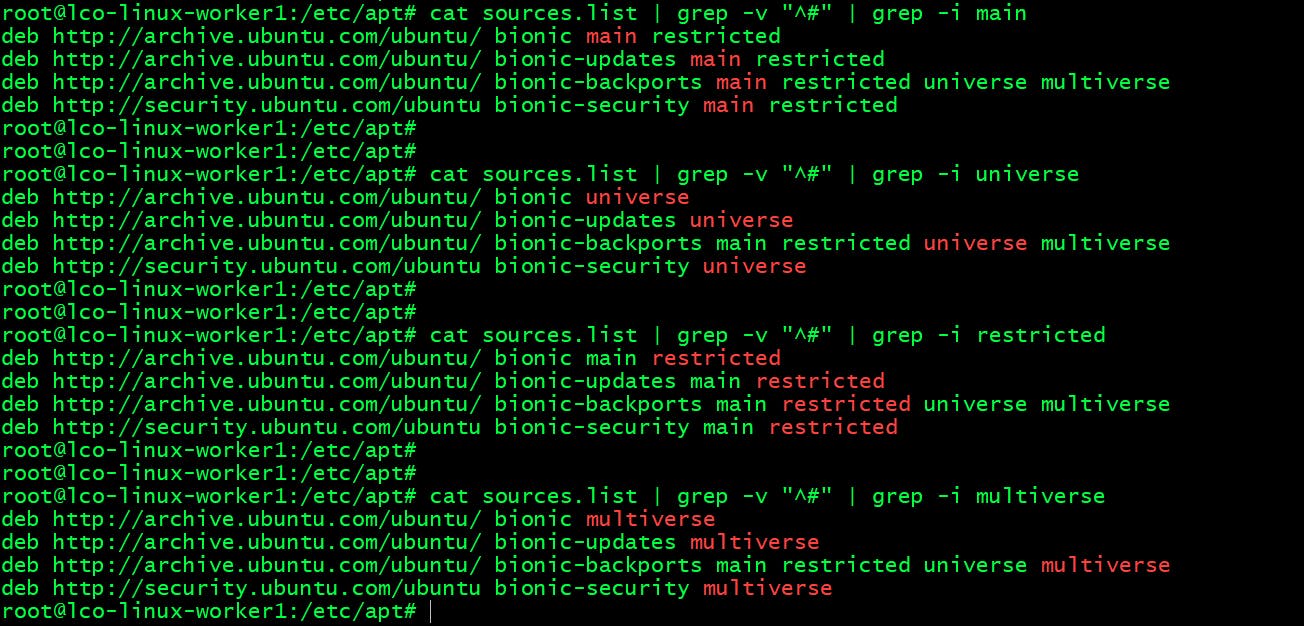
There are four main repositories on Ubuntu systems:
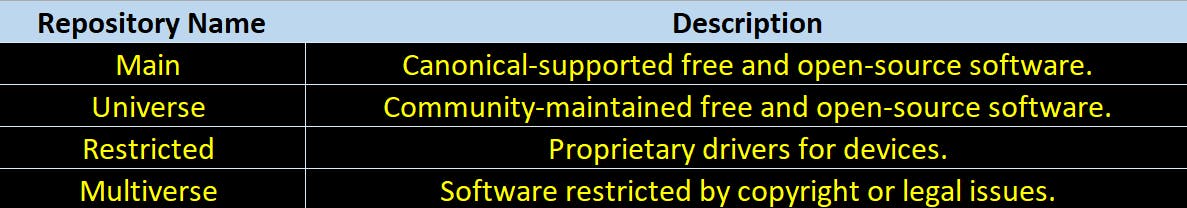
This is how these repositories are configured in sources.list file.
cat sources.list | grep -v "^#" | grep -i main
cat sources.list | grep -v "^#" | grep -i universe
cat sources.list | grep -v "^#" | grep -i restricted
cat sources.list | grep -v "^#" | grep -i multiverse
Each line starting with deb or deb-src adds a package repository on your Linux system.
deb ->
These repositories contain binaries or precompiled packages. These repositories are required for most users.
deb-src ->
These repositories contain the source code of the packages. Useful for developers.
To understand a repository entry in sources.list file let us take an example entry here.
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted
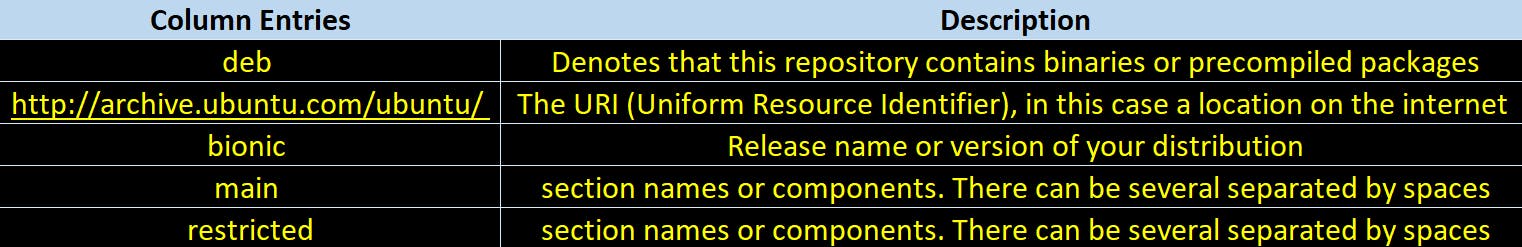
Web locations of these repositories ->
Attaching few snapshots from the web url's of these repositories.
archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ubuntu
archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ubuntu/ubuntu/ubu..
archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ubuntu/ubuntu/ubu..
Adding custom repositories on Ubuntu
We need to configure custom repositories for the applications which are natively not available with Ubuntu's official repositories which we have discussed above.
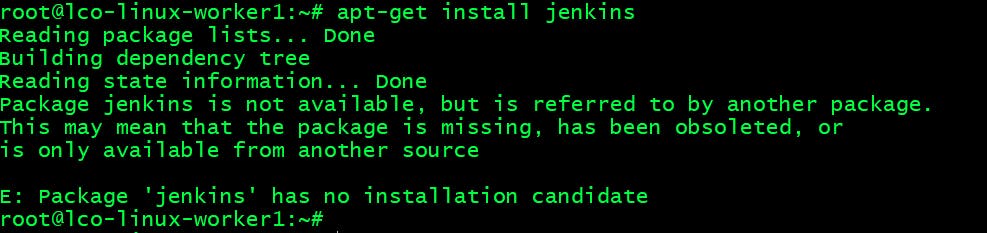
Here we will add Jenkins repository to our Linux system. Before adding the repository if you try to install the Jenkins package you will get the following error:
Run the following commands to add it to our system.
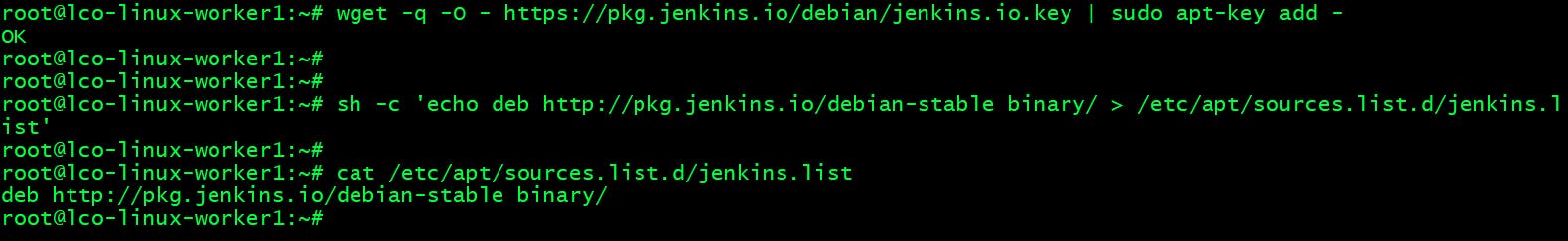
Step 1 -> Import the public key used by the package management system
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
Step 2 -> Create a list file and add repository config for Jenkins
sh -c 'echo deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
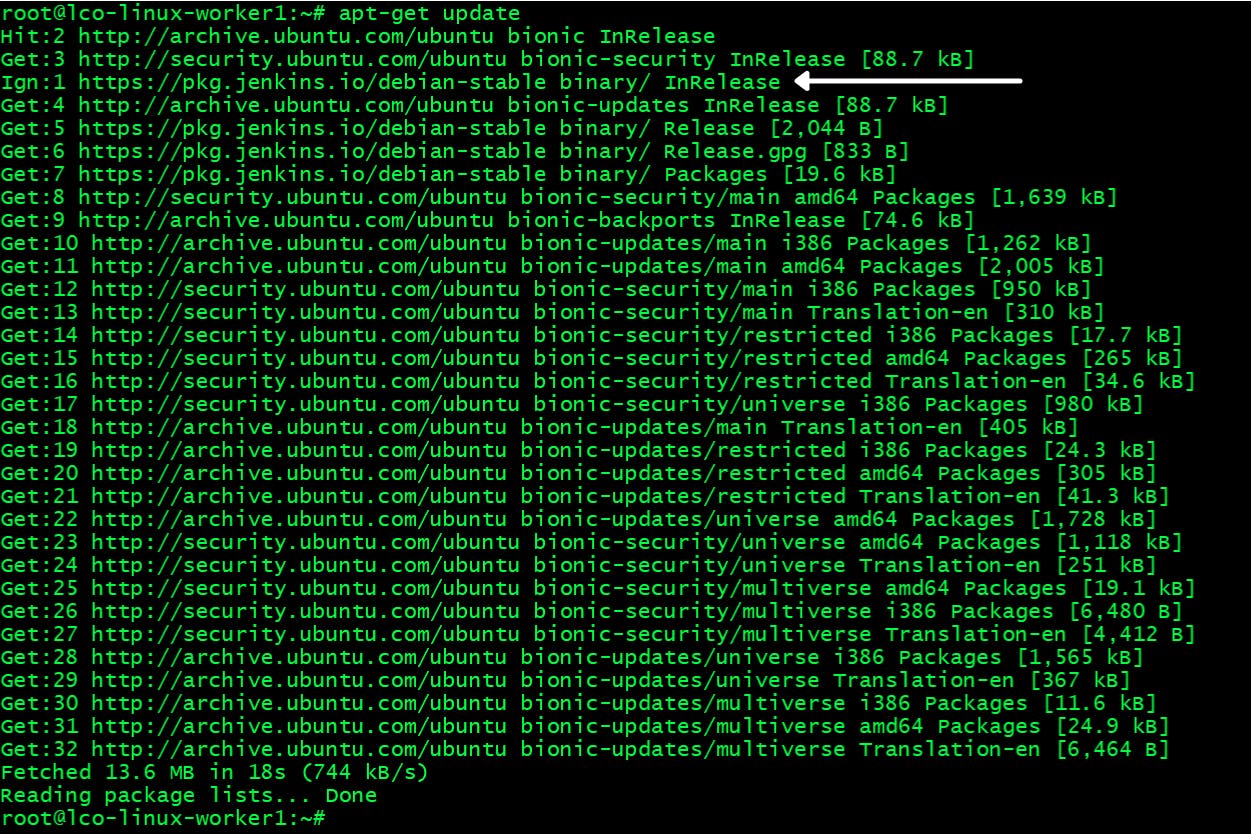
Step 3 -> Update the repositories Run the following command which reload the database for local package on all the repositories.
apt-get update
Now try to install the Jenkins package.
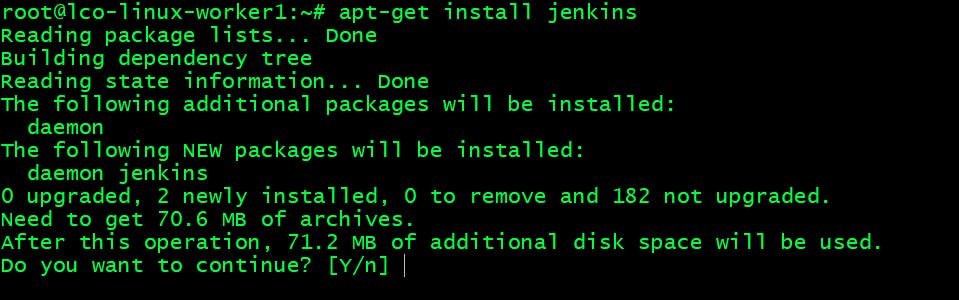
You can add Repositories with
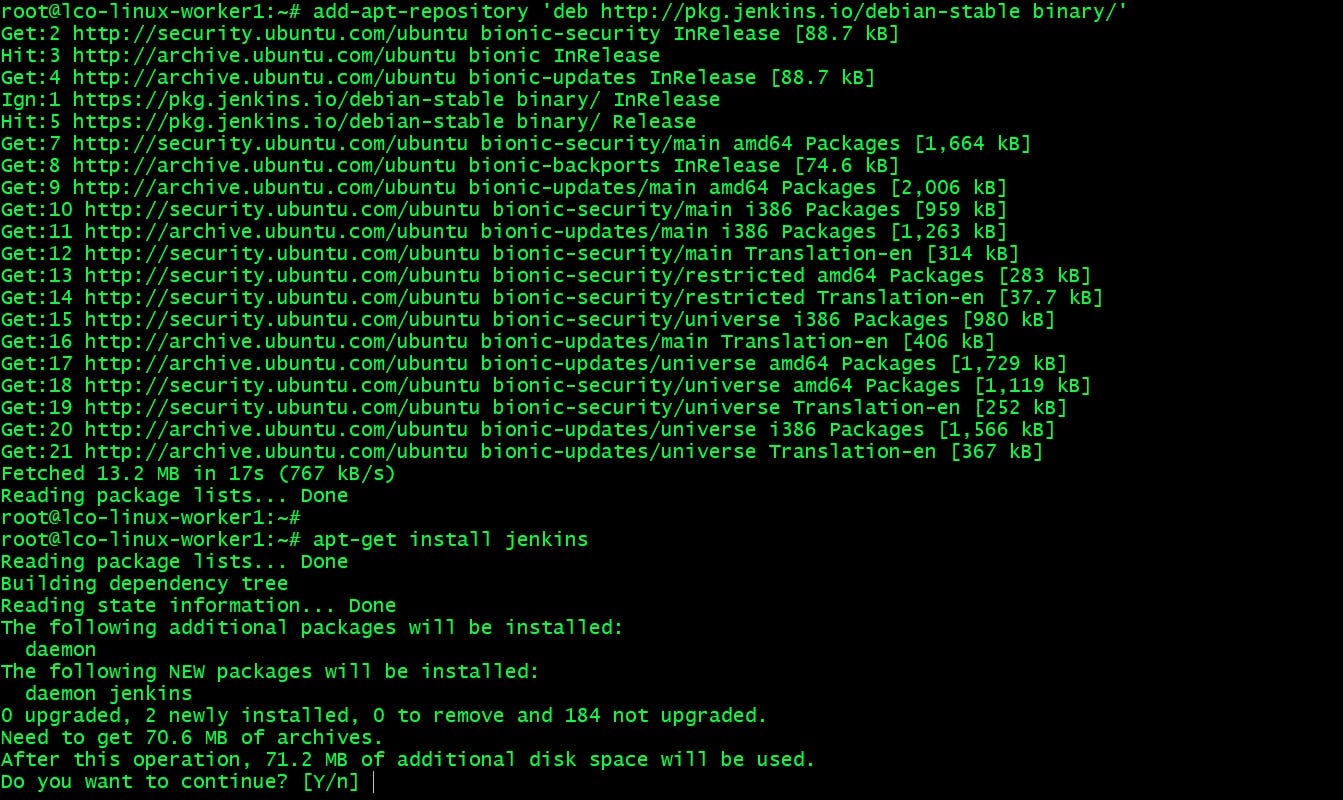
add-apt-repositorycommand as well. The repository will be appended to sources.list file. The syntax would be like this -add-apt-repository [options] repositoryFor example:
add-apt-repository 'deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/'
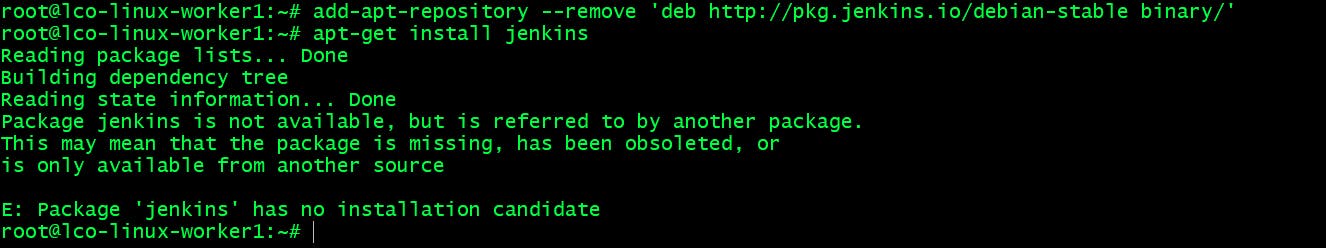
In order to remove a custom repository the command syntax would be like this:
add-apt-repository --remove repositoryFor example:
add-apt-repository --remove 'deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/'
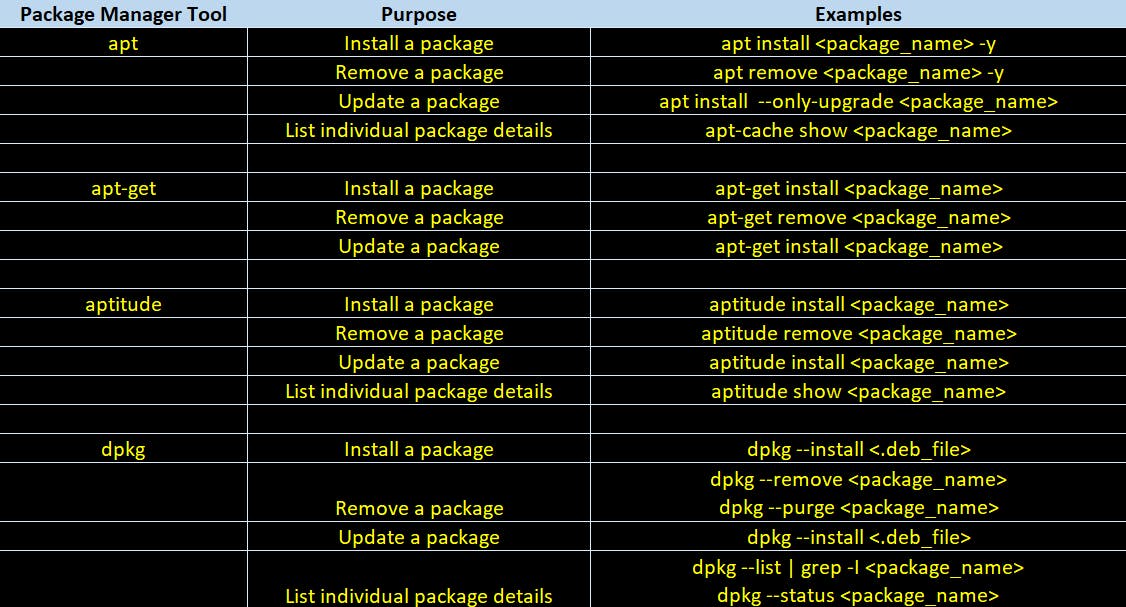
Package Manager Tools on Ubuntu
There are four type of package manager tools exists on Ubuntu.
Below table briefly introduces them.

Package Manipulation commands on Ubuntu
Below table introduces commands to perform various package related operations on Ubuntu Linux.
Package Management on CentOS Linux
On Red Hat Linux / CentOS distributions we can do package management through CLI and from the GUI as well. Here I will demonstrate the CLI way of doing this.
Configuring Software repositories on a CentOS System
I am using CentOS Linux 7 system for this demo purpose.
The place to configure software repositories on CentOS is /etc/yum.repos.d directory. The name of the files must end with .repo extension.
Here is a sample repo file:
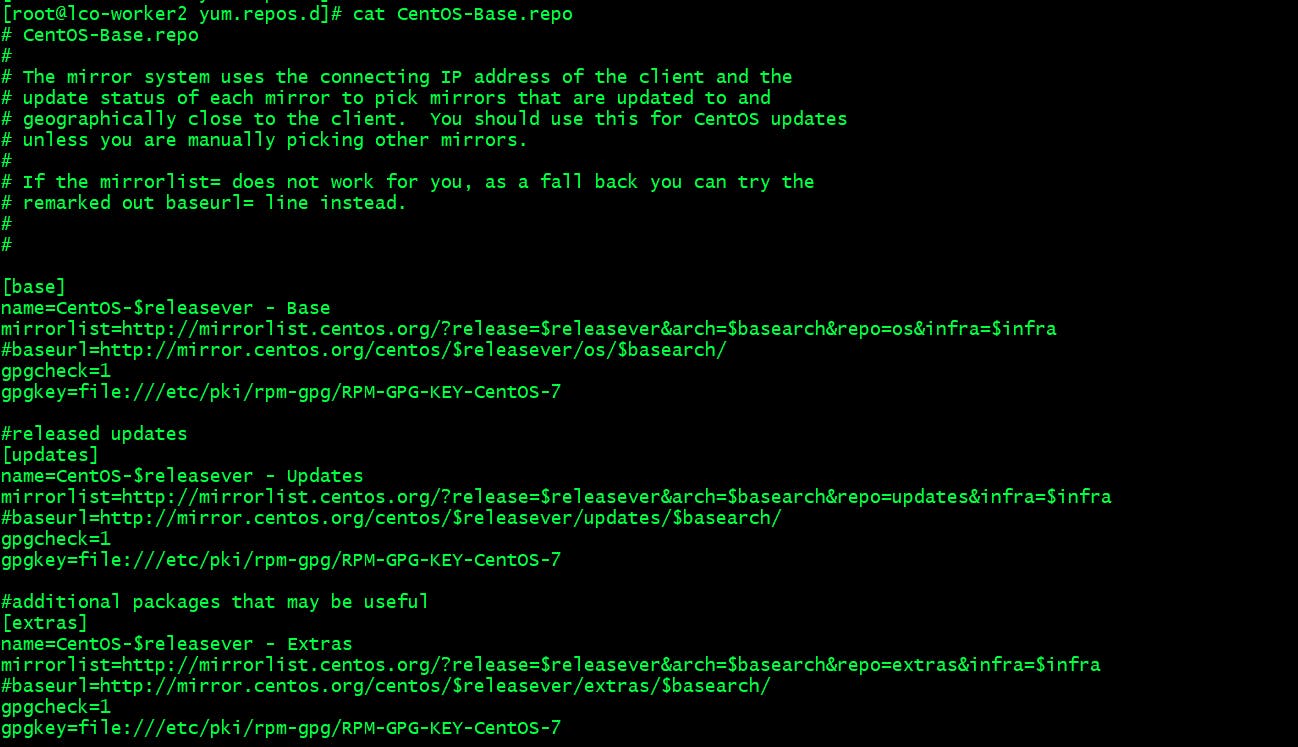
Lines starting with hash (#) are comments which are used for documentation purposes. Comments can also be used to disable a certain package repository.
Adding custom repositories on CentOS Linux
We need to configure custom repositories for the applications which are natively not available with CentOS's official repositories.
Here we will add EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository to our Linux system. It is an additional package repository which enables us to install packages for commonly used software.
Install EPEL Repo via yum ->
Run the following commands to install epel repository on your CentOS Linux system.
Here we are using yum which a Package Manager tool on Red Hat based systems. We will learn more about it in next section.
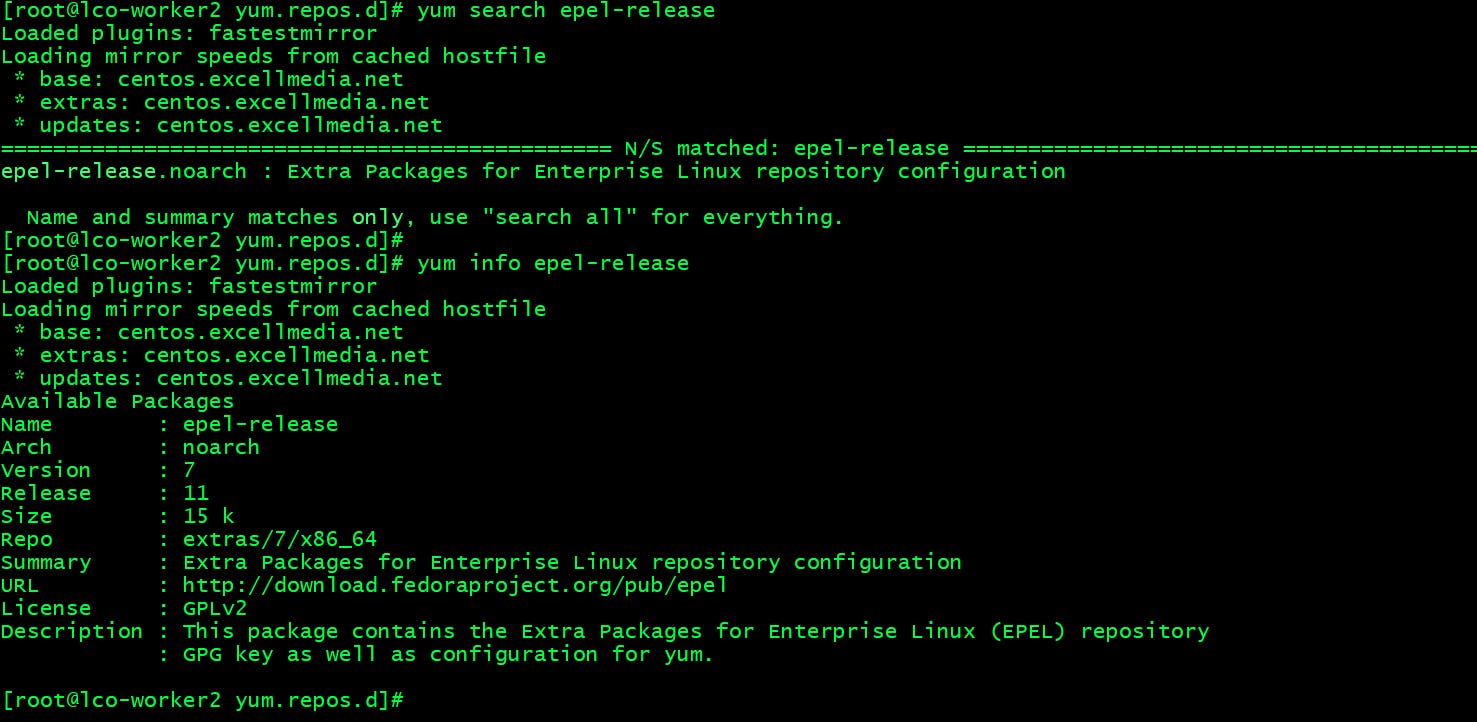
Search and get information about the epel-release package.
yum search epel-release
yum info epel-release
Now Install the epel-release package.
yum install -y epel-release
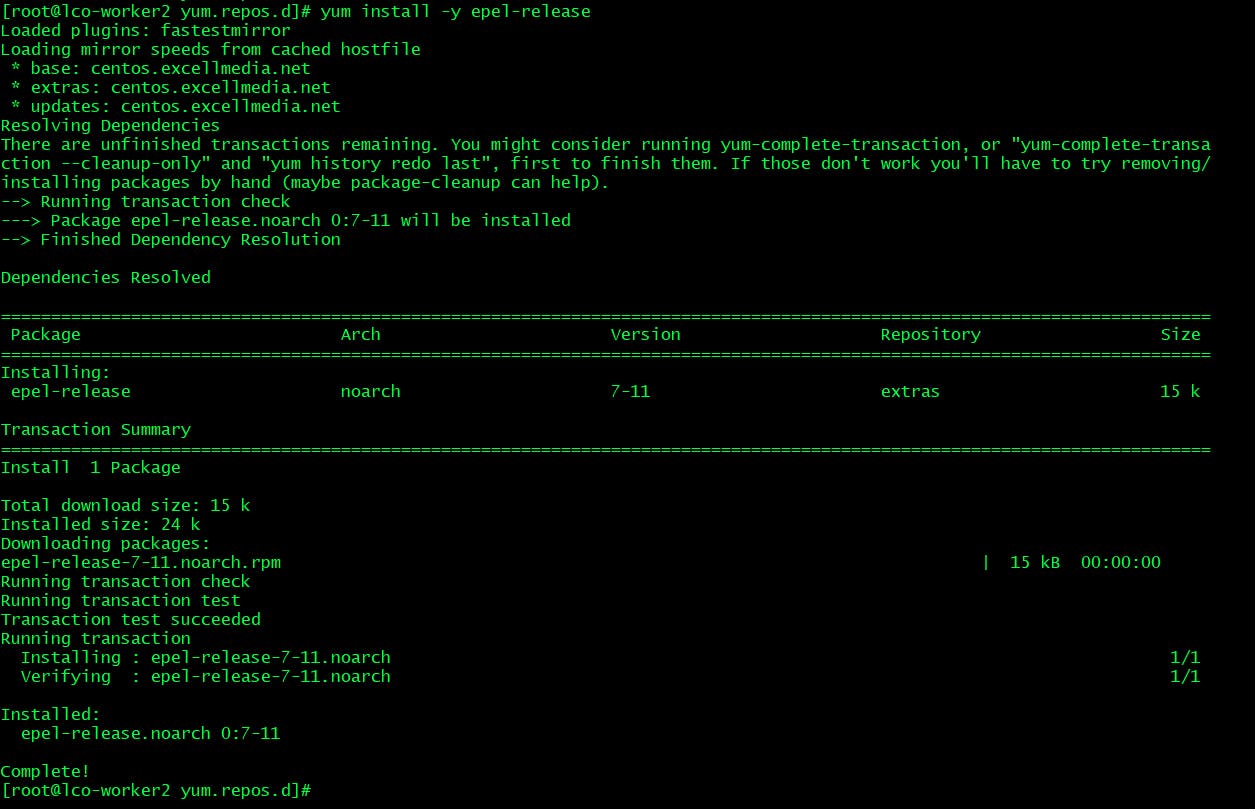
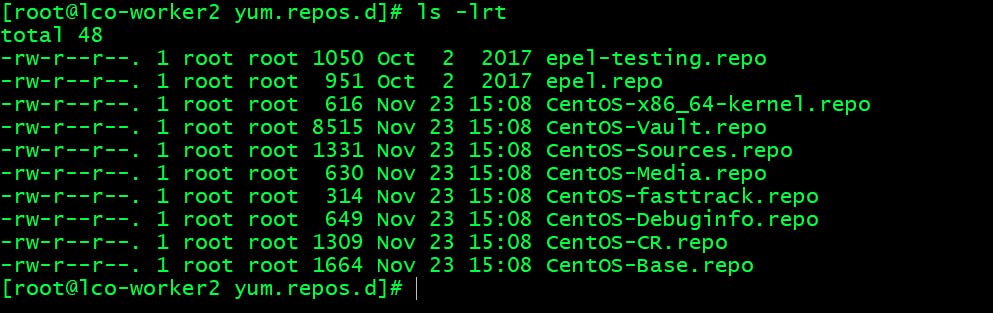
Now you will find epel repo files under /etc/yum.repos.d directory.
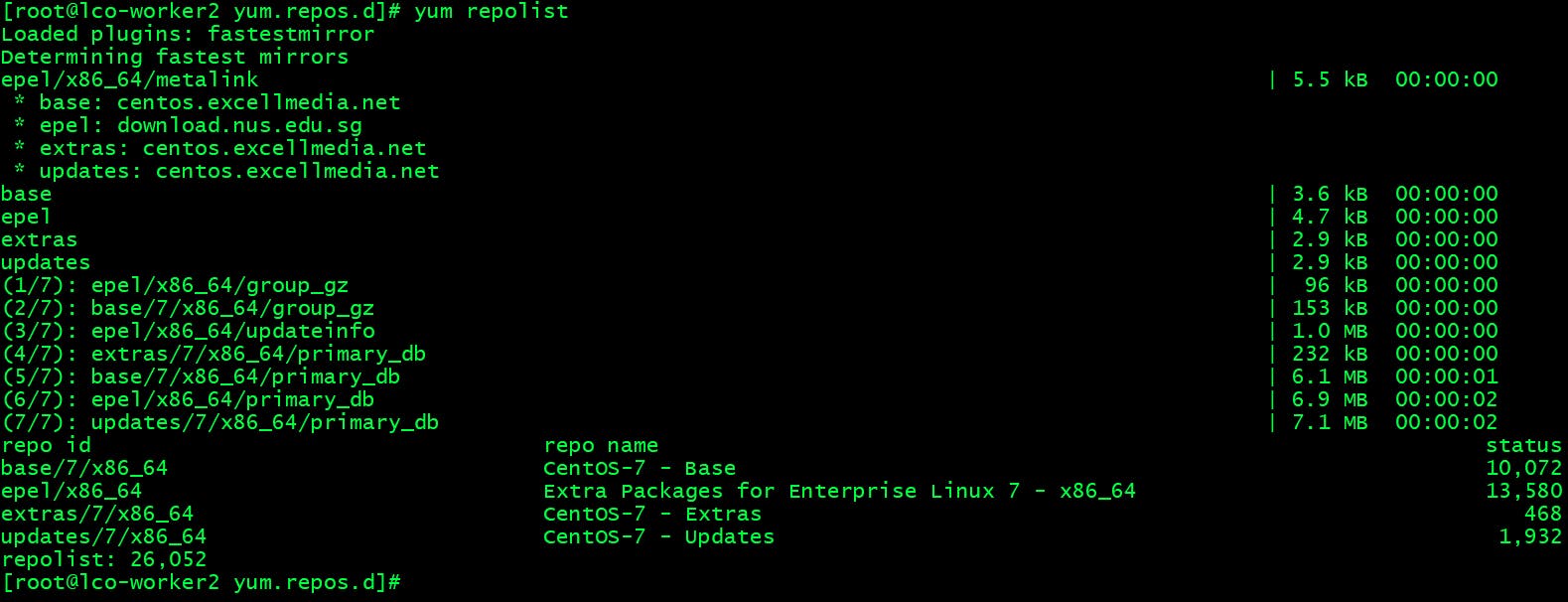
Verify the EPEL Repo Installation: Run the following command to verify the repo installation.
yum repolist
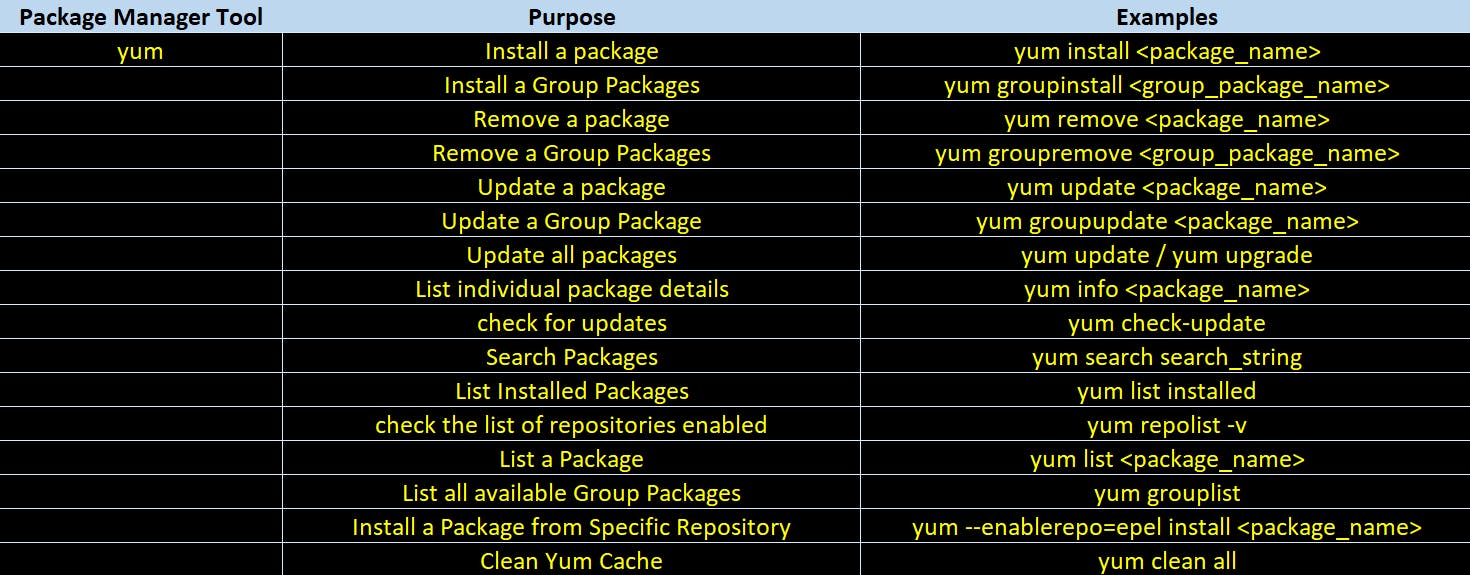
Package Manager Tools on CentOS
There are three type of package manager tools exists on CentOS.

dnfis default package manager since Fedora 22 in 2015 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.
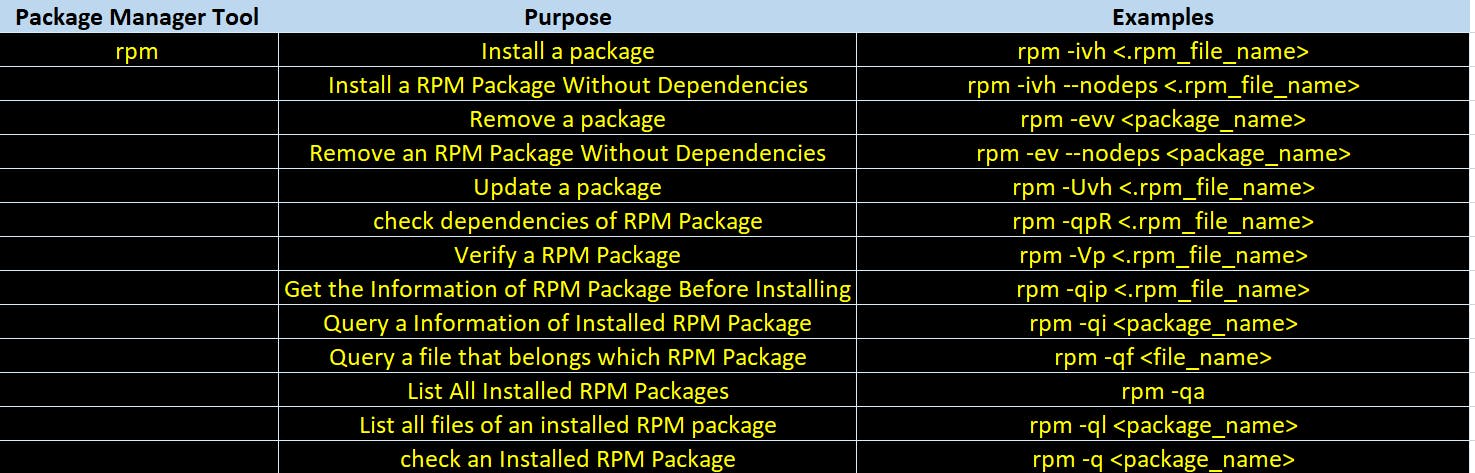
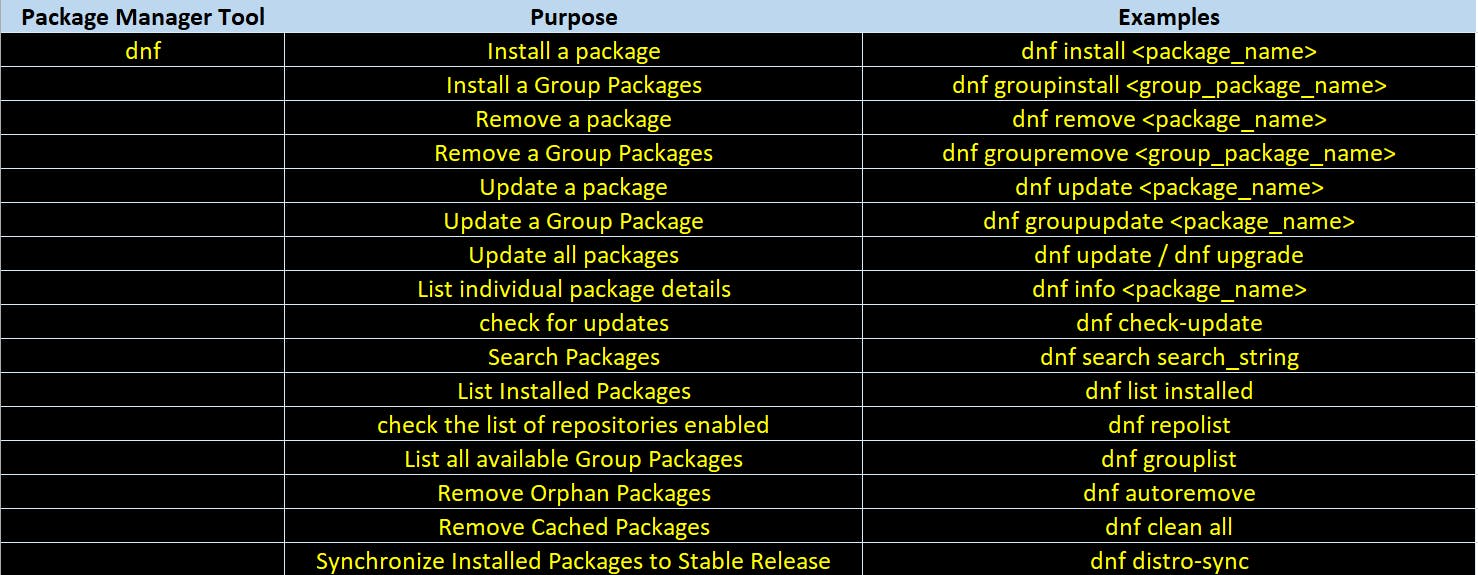
Package Manipulation commands on CentOS
Below tables introduces commands to perform various package related operations on CentOS Linux using different package management tools.
Syntax to import
gpg keyson CentOS Linux systems is ->
rpm --import <key_file_path>
Using yum-config-manager in RHEL/CentOS Linux
yum-config-manager is a tool to manage yum configuration options and yum repositories.
Add repository with yum-config-manager ->
yum-config-manager --add-repo http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo

Enabling a yum Repository using yum-config-manager ->
Run the following command to enable a yum repository.
yum-config-manager --enable jenkins
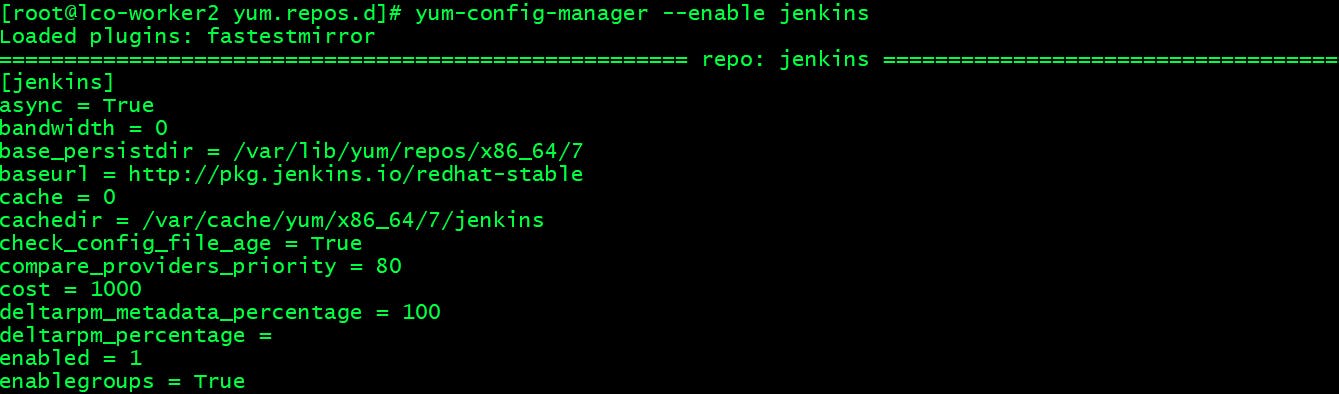
You can see the enabled parameters value is set to 1.
Disabling a yum Repository using yum-config-manager ->
Run the following command to disable a yum repository.
yum-config-manager --disable jenkins
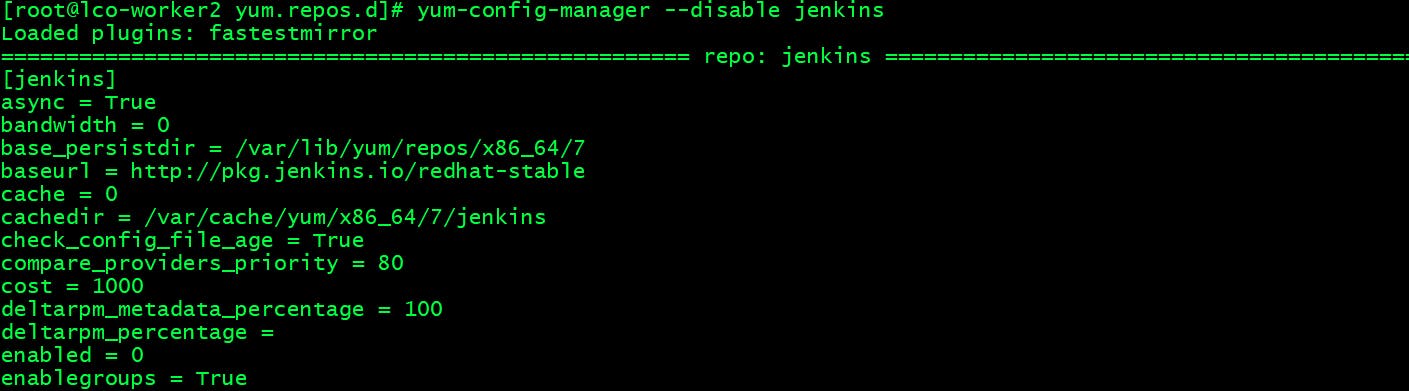
You can see the enabled parameters value has been changed to 0 from 1.
That's all for this detailed guide covering all aspects of Package and Repository Management on Linux systems.
Hope you like the article. Stay Tuned for more.
Thank you. Happy learning!
